The research objectives and expected outcome
The project deals with the approval of machine learning (ML) technology for systems intended for use in safety-related applications in all domains covered by the EASA Basic Regulation (Regulation (EU) 2018/1139).
Data-driven learning techniques are a major opportunity for the aviation industry but come also with a significant number of challenges with respect to the trustworthiness of ML and deep learning (DL) solutions.
EASA published its Artificial Intelligence Roadmap in February 2020, followed by a first major deliverable, a Concept Paper ‘First usable guidance for level 1 machine learning applications’ in December 2021. This concept paper lays down the basis of EASA future guidance for ML applications approval thanks to a W-shaped process and identifies a number of areas in which further research is necessary to identify efficient and practicable means of compliance with the defined ‘AI trustworthiness’ objectives.
MLEAP project is a research project initiated by EASA and funded under the Horizon Europe framework. MLEAP has been tailored to investigate the challenging objectives of the W-shaped process at the core of EASA AI Concept Paper.

The intended short-term effect of this project will be to streamline the certification and approval processes by identifying concrete means of compliance with the learning assurance objectives of the EASA guidance for ML applications (levels 1, 2 and 3 as defined in the EASA AI Roadmap), with a specific focus on Level 1B and Level 2.
The achieved medium-term effect of the project will be to alleviate some remaining limitations on the acceptance of ML applications in safety-critical applications.
The requested output
The research results will be a set of reports identifying a set of methods and tools to address the following three important topics:
• Guarantees on ‘machine learning model generalisation’
• Guarantees on ‘Data completeness and representativeness’
• Guarantees on algorithm and model robustness
The reports will highlight a set of anticipated concepts for the evaluation and certification of AI-based systems supporting the EASA roadmap deliverables, and help industry stakeholders in planning new strategies for deploying AI in their human and technical organisations.
Along with the project, three aviation use-cases will be developed to demonstrate the effectivity and usability of the proposed methods and tools. They will be developed to demonstrate the effectivity and usability of the proposed methods and tools. Those use cases should be developed in a software and hardware environment, accessible remotely by EASA or through software package deliveries to EASA. The essential life cycle artefacts developed in the project to address the different steps of the W-shaped process should be made available to EASA.
The work break-down structure of this project is the following:
• Task 1: Methods and tools for the assessment of completeness and representativeness of data sets (training, validation, and test) in data-driven ML and DL
• Task 2: Methods and tools for quantification of generalisation guarantees for ML and DL models
• Task 3: Methods and tools for the verification of an ML algorithm and model robustness/stability
• Task 4: Communication, dissemination, knowledge-sharing, stakeholder management
• Task 5: Project management
MLEAP timeframe is established to support key EASA AI programme milestones as depicted in figure below:
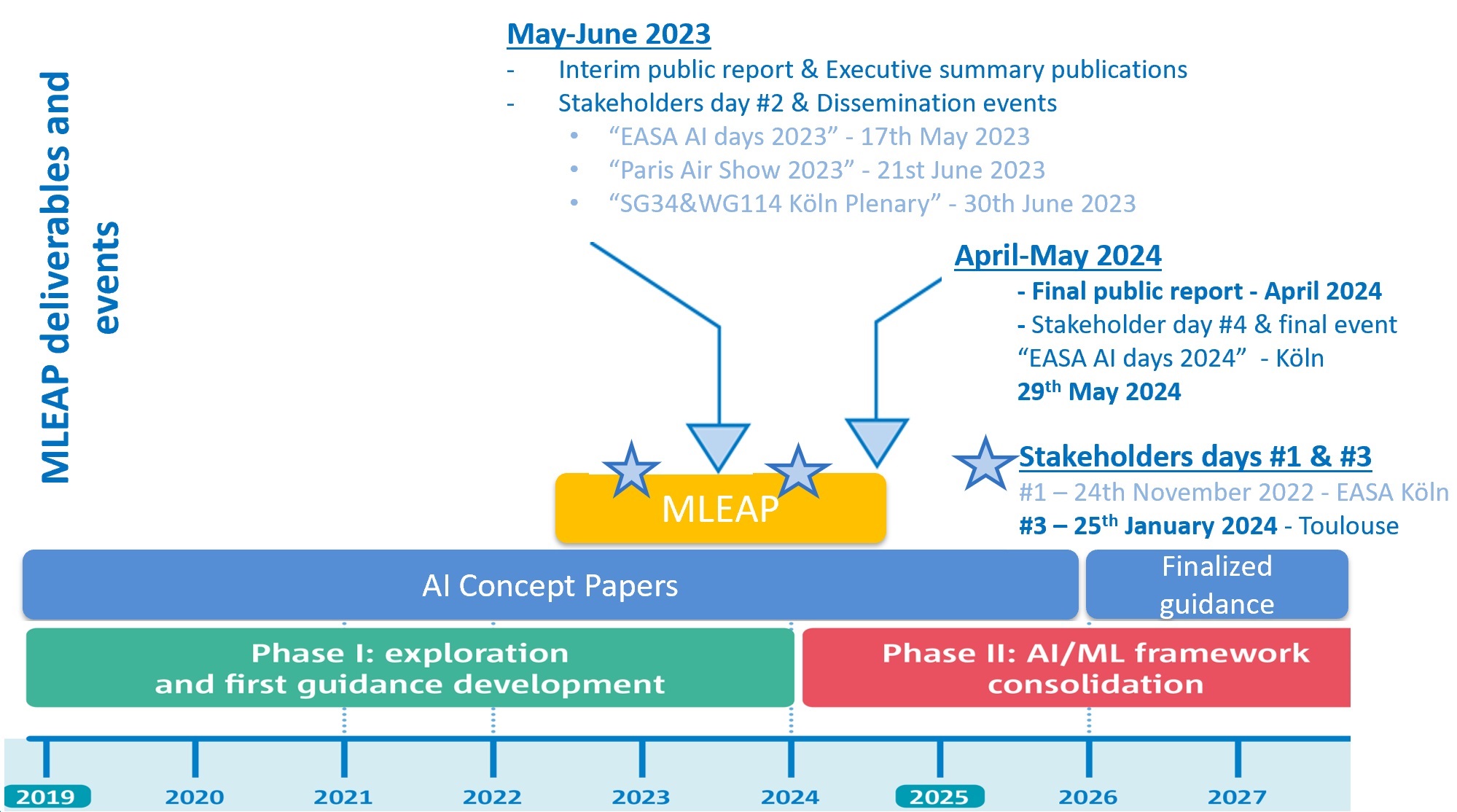
First MLEAP public deliverable
Halfway through the project, the MLEAP consortium published its interim report on Thursday 11 May 2023. This 258-page report provides a detailed state of the art for the three tasks of interest of MLEAP, a selection of the most promising methods and tools to be explored, and a description of the aerospace use cases that will be used to evaluate these selected methods and tools. Preliminary results of this interim report have already been used to enrich EASA AI concept paper issue 2 currently under public consultation.
One of the main results is a first version of a general framework to cover most of the ML-related steps the W-shaped process of the EASA AI Concept paper.
This process will be further refined in the next phases of the project based on the first experimentation and the interim report findings related to the data evaluation and preparation (Chapter 3) and considering recommendation about robustness and performance stability evaluation (Chapter 5).
MLEAP project will now proceed with evaluating the selected methods and tools to the three aeronautical AI use cases (Chapter 2) retained for the project:
- Speech to text in Air Traffic Control communication
- Drone collision avoidance (ACAS-XU)
- Vision-based maintenance inspection
The results for the EASA - Collins Aerospace ”Formula” IPC report published in April 2023, related to the identification of formal methods approaches as efficient means to meet certification objectives from the EASA AI concept paper, will also be considered in the next steps of the project, in particular for MLEAP Task 3.
This interim report will be presented and discussed during public events in May and June (see Recent MLEAP public events Section below).
Final MLEAP Report
Building on previous MLEAP deliverables, the Final Report gathers the findings and in-depth analyses of all four phases of the Project into a comprehensive document.
The Report details the project's overarching methodology, as well as the aviation use cases examined throughout the Project before delving into the three technical tasks of the Project, adhering to the same systematic approach. This approach involves the identification of promising methods and tools from an extensive state of the art, followed by their preliminary testing on toy use cases, and subsequently, the validation of those primary results on complex aviation use cases.
Finally, a generic development pipeline and recommendations are proposed by the MLEAP consortium as a practical implementation of the EASA W-shape development process.
An Executive Summary of the Final Report is also available and provides an overview of the Project key findings.
Quoting this report:
MLEAP Consortium, EASA Research – Machine Learning Application Approval (MLEAP) Final Report, May 2024
Past MLEAP public events
-
EASA AI Days 2024 - MLEAP Final dissemination event – July 3, 2024 – Cologne
-
Presentations
-
-
Recordings
Video recording Day 1 — EASA Artificial Intelligence Days — High-Level Conference 2024
Video recording Day 2 — EASA Artificial Intelligence Days — High-Level Conference 2024
- January 25, 2024 Airbus Toulouse during Stakeholder day #3
Presentation of the latest development of MLEAP project - see presentation
Recordings of some MLEAP conferences will be made available on the Airbus protect Youtube channel.
- June 30 , 2023 - Eurocae WG-114 and SAE G-34 "Artificial Intelligence in aviation" working group
EASA and MLEAP consortium presented the interim report results and perspectives beyond MLEAP project - see presentation
- June 21, 2023 - MLEAP at the Paris Airshow
Awareness session Conference: June 21 from 10 to 11am - at Airbus Pavillon.
Knowledge Sharing Conference & Networking: June 21 from 3 to 5pm - at VIPARIS Conference center - Conference room N°2 - This conference was virtual and on-site.
The agenda and information about this year's Paris Airshow can be found on this dedicated page. A recording of the presentation was made available on the Airbus protect Youtube channel.
-
May 17, 2023 - EASA Artificial Intelligence Days
This was an opportunity to present and answer questions of interested parties on the first public deliverables of the MLEAP project, which were published in May 2023 on this page. The agenda and recording of the conference can be found on the EASA AI days 2023 event page.
- November 24 2022 Stakeholders day 2022
On Thursday 24 November 2022, the first dissemination event of the MLEAP project, which, was held at EASA. The aim of this "Stakeholders Day 2022" was to present in detail the objectives of the project to the various parties (aircraft and ATM/ANS system designers, aircraft manufacturers, certification specialists, authorities, standardisation bodies) directly interested in the results of this research project.
Around 60 participants with different backgrounds attended this hybrid event. The EASA AI team briefed the audience with its vision, and how the MLEAP project will deliver on the AI roadmap, before the MLEAP consortium presented the project workplan, the objectives of each technical task and the first results achieved. Stakeholders' reactions and questions were collected in a Q&A session and will serve as an input in future phases of the project. Get the meeting material.
Research Project details
 This project will be funded from the European Union's Horizon Europe
This project will be funded from the European Union's Horizon Europe
research and innovation programme.
At Airbus Protect
Project manager: Michel Kaczmarek, Michel.Kaczmarek [at] apsys-airbus.com
Technical lead: Olivier Galibert, Olivier.Galibert [at] lne.fr
Consortium members
Numalis and LNE.
At EASA
Project manager: Willy Sigl, willy.sigl [at] easa.europa.eu
Technical lead: Xavier Henriquel, xavier.henriquel [at] easa.europa.eu
Task 1 lead – Representativeness and completeness – François Triboulet, francois.triboulet [at] easa.europa.eu
Task 2 lead – Generalization guarantee – Xavier Henriquel, xavier.henriquel [at] easa.europa.eu
Task 3 lead – Model robustness and stability – Guillaume Soudain, guillaume.soudain [at] easa.europa.eu