Can I fly my drone anywhere I want to?
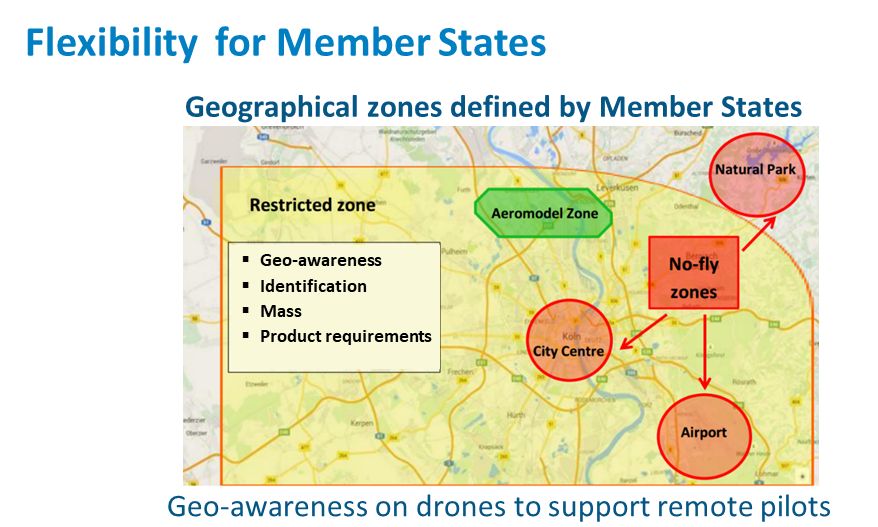 Each EASA Member State will determine drone geographical zones, which are areas where drones may not fly (e.g. national parks, city centres or near airports) or may fly only under certain conditions, or where they need a flight authorisation. Therefore, it is important for you to consult your National Aviation Authority to check where you can and cannot fly your drone.
Each EASA Member State will determine drone geographical zones, which are areas where drones may not fly (e.g. national parks, city centres or near airports) or may fly only under certain conditions, or where they need a flight authorisation. Therefore, it is important for you to consult your National Aviation Authority to check where you can and cannot fly your drone.
These geographical zones apply to all categories.
In addition, you are not allowed to fly a drone close to or inside an area where there is an ongoing emergency response.
See the links to National Aviation Authorities at:
https://www.easa.europa.eu/domains/civil-drones/naa
Regulatory reference: Article 15 and UAS.OPEN.060 (4) of EU regulation 2019/947.
Can I fly over people?
Generally when you operate in the ‘open’ category, you are not allowed to fly over uninvolved people, unless you have a privately built drone with a weight below 250 g or a drone purchased on the market with a class identification label0 or 1 mark. In any case, try to minimise the time during which you fly over people.
If you have a drone with a CE class 2 mark, under subcategory A2, as a general rule, keep the UA at a lateral distance from any uninvolved person that is not less than the height at which the drone is flying (this is the ‘1:1 rule’, i.e. if the UA is flying at a height of 40 m, the distance from any uninvolved person should be at least 40 m), and never fly closer than 30 metres horizontally from any uninvolved person. If your drone is equipped with a low-speed mode function and this is active, you can fly as close as 5 metres from uninvolved people.
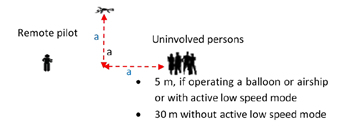
Distance from uninvolved people in the case of flying with a class C2 drone
In all other cases (drones with class identification label3, 4, 5 or 6 marks or privately built and heavier than 250 g), you need to ensure that no uninvolved people are present within the range of the operation.
Regulatory reference: article 4 (1) (c) and UAS.OPEN.040 of EU regulation 2019/947.
How high can I fly my drone?
Your maximum flight height is generally 120 m from the earth’s surface. Please check whether the National Aviation Authority imposes a geographical zone with a lower limit in the area where you fly. If you need to fly over an obstacle taller than 120 m, you are allowed to fly up to 15 metres above the height of the obstacle, but only if there is an explicit request from the owner of the obstacle (e.g. a contract with the owner to perform an inspection). In such a case, you may fly within a horizontal distance of 50 metres from the obstacle.
When you are operating in hilly environments, the height of the drone above the surface of the earth should be within the grey zone in the picture below: you need to keep the drone within 120 m of the closest point of the terrain. This means that there may be conditions such as on top of a hill where even if you keep your drone 120 m from the side of the hill, you are actually flying at a distance higher than 120 m above the bottom of the valley. So as long as you keep your drone within 120 m of the shoulder of the hill (as in the grey area in the picture below), your flight is legal.
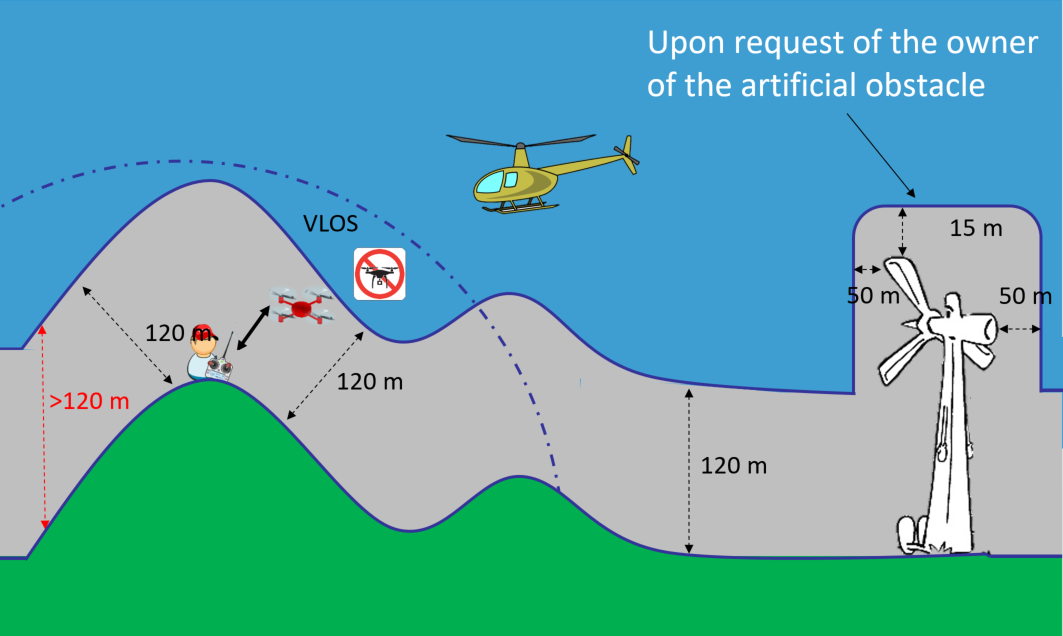
Regulatory reference: UAS.OPEN.010 (2) (3) Annex Part A of EU Regulation 2019/947