Standardisation, monitoring the way in which each Member State applies the common EU rules on aviation safety, is one of EASA’s core task. Each Member State has set up one or more Authorities responsible for the safety oversight of civil aviation activities within their territory. EASA standardisation activities set out to ensure that:
- the travelling public enjoys a high and uniform level of aviation safety across the EU,
- the EU aviation industry benefits from a level playing field (the EU single market),
- approvals and certificates issued by EU Authorities are mutually recognised and trusted, and
- the European system is recognised by its international partners.
What countries / states are part of the system?
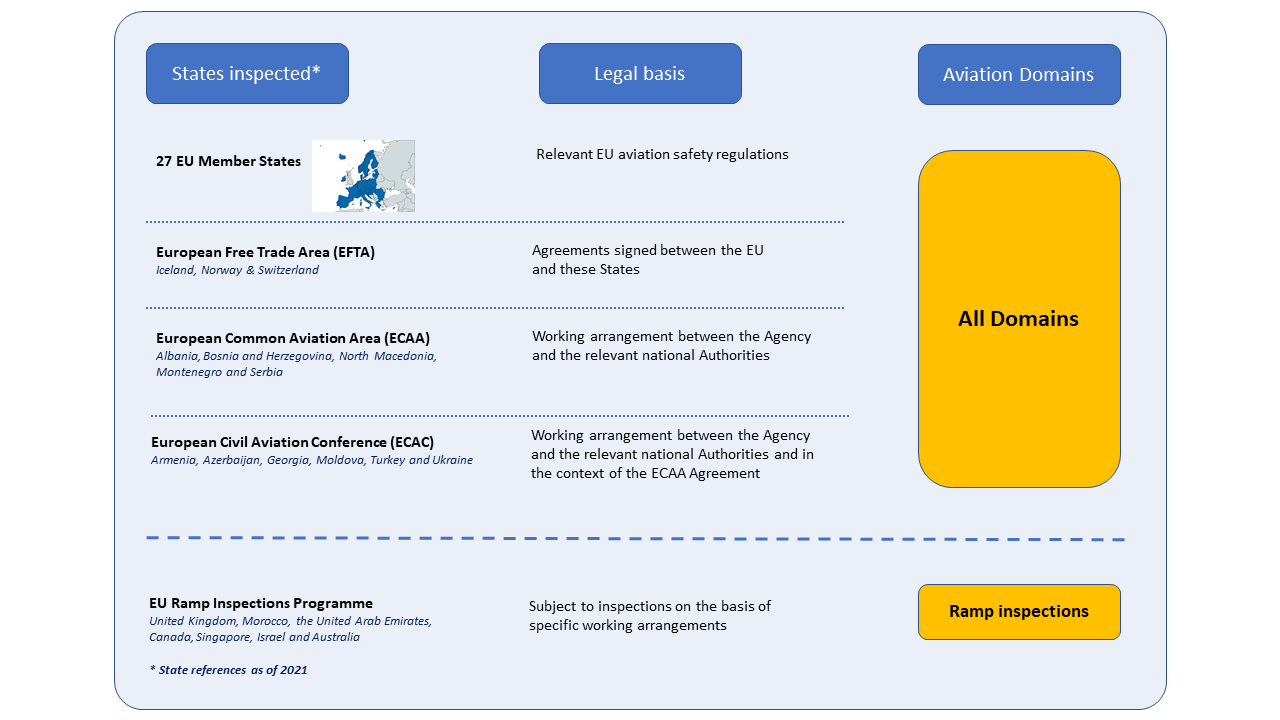
EASA conducts standardisation activities in all EU Member States, as well as in Switzerland, Norway and Iceland. Certain non-EU States applying the EU aviation safety rules in specific domains are also subject to inspections.
Check out the schematic that explains what states are inspected under what legal basis (click on image to open as PDF).
Standardisation activities – what do they cover?
The Agency conducts two types of activities, as defined in the Standardisation Regulation:
- Inspections of national Authorities, carried out by multi-national teams of aviation experts. Such inspections normally include a sampling of organisations (airlines, maintenance organisations, etc) that are under the oversight of the inspected Authority.
- Continuous monitoring of the application by national Authorities of the EU aviation safety regulations. Such continuous monitoring activities (CMA) are based on a data-driven assessment of the Authorities’ ability to discharge their safety oversight responsibilities, using a wide range of data collected from multiple national and international sources.
The continuous monitoring activities are the overarching element: they determine the prioritisation, frequency and scope of standardisation inspections, with the help of a decision support tool (the “Standardisation Model”) that uses all data collected to determine a “standardisation rating” to each Member State in each aviation domain.
There is more to Standardisation
Besides inspecting and monitoring, a significant part of EASA’s standardisation activities concentrates on supporting and assisting EU national Authorities in fulfilling their tasks to maintain a safe environment for civil aviation in their countries.
National Standardisation Coordinators from all States come together on a regular basis to exchange ideas and good practices, discuss challenges, and help to maintain a strong and just standardisation culture.
The inspection phases
Each standardisation inspection is split into three phases: 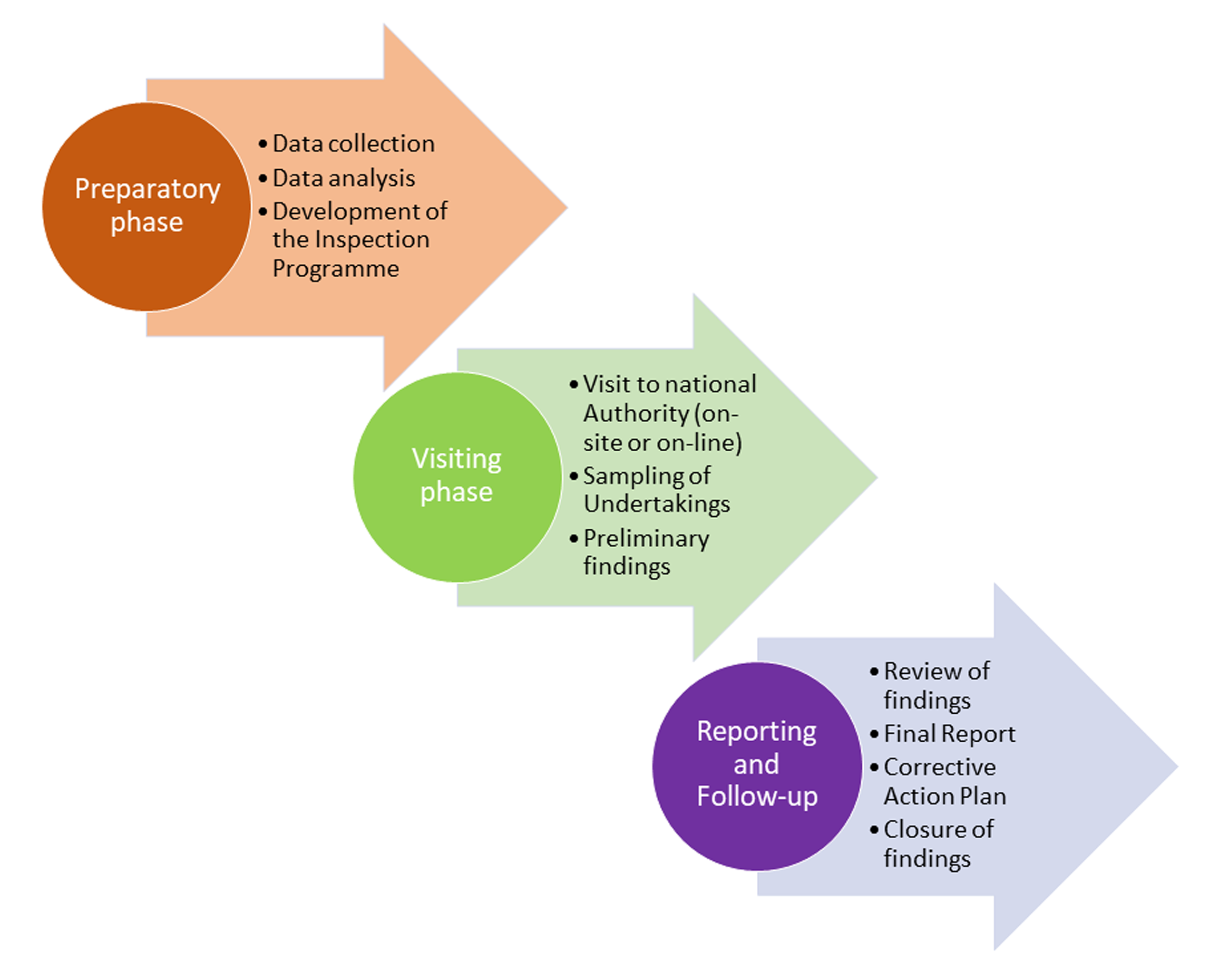
- preparatory phase,
- visiting phase, and
- reporting & follow-up phase.
Procedures, guidelines and tools ensure that all inspections follow the same approach and have the appropriate level of scrutiny.
Have a look at the overview to see what is covered (click on image to open as PDF).
Adapting to new challenges: COVID-19
During the COVID-19 pandemic, EASA had to rethink its way of conducting standardisation activities. As significant travel and gatherings’ restrictions were put in place, the Agency re-focused its priorities on continuous monitoring, in order to detect and address any emerging safety issue as a consequence of the crisis. The technical expertise of standardisation inspectors was also redeployed to provide recovery support to national Authorities, as part of the Agency’s project “Return to Normal Operation (RNO)”.
In parallel, the Agency developed a methodology to conduct standardisation inspections remotely, allowing the resumption of inspections. Remote inspections are a new working method where the interaction between EASA and the inspected Authority takes place using modern technologies. Review of documents and records, interviews with staff, and direct observation, take place over a remote connection, using suitable audio- and video-communication tools, and sharing files and data online.
Meet the inspection teams!
EASA and national Authorities’ staff are working closely together during standardisation activities, and form a strong partnership.
Inspection teams are led by an EASA team leader, with qualified inspectors from EASA and other national Authorities complementing the team and contributing with their expertise to the standardisation network. In a typical year, EASA performs around 100 standardisation inspections across all EU Member States, involving around 40 staff members and with the support of around 100 team members seconded from national Authorities.
Comprehensive training and qualification programmes ensure that standardisation teams maintain the necessary level of expertise and knowledge to carry out these activities.
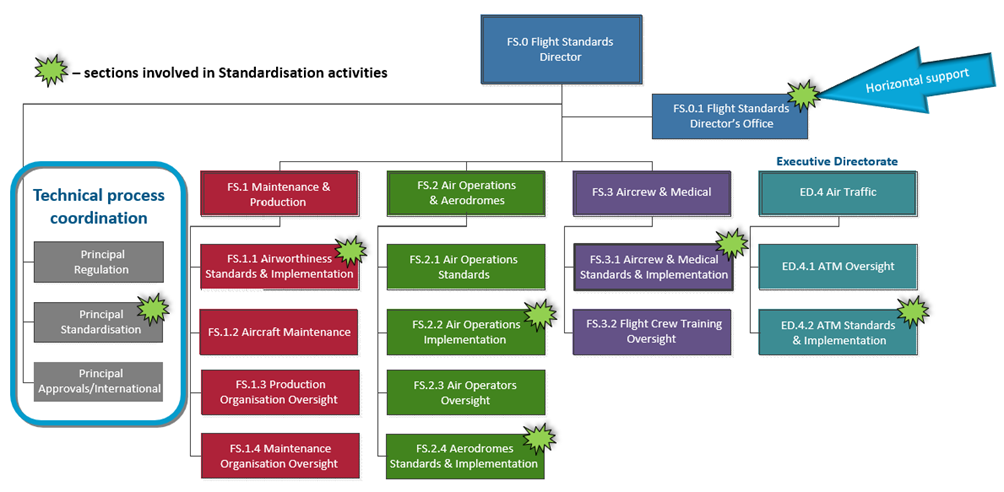
EASA staff dealing with standardisation activities are located in the Flight Standards and Executive Directorates at EASA.
All standardisation activities are coordinated by a Principal Coordinator, reporting to the Flight Standards Director and supported by a team located in the Director’s Office (click on image to open as PDF).