Specialised operations (SPO) means any operation other than commercial air transport where the aircraft is used for specialised activities such as:
- agriculture
- construction
- photography
- surveying
- observation and patrol
- aerial advertisement
Specialised operations are governed by Commission Regulation (EU) No 965/2012 on air operations. They have been introduced into the EU set of harmonised rules through Regulation (EU) No 379/2014 that amends Regulation (EU) No 965/2012 on air operations by complementing it with Part-SPO.
Regulation (EU) No 379/2014 was adopted by the European Commission on 7 April 2014 and published in the Official Journal of the European Union on 24/04/2014. Regulation (EU) No 379/2014 applies from 1 July 2014. A horizontal opt-out lasted in the majority of Member States until 21 April 2017, meaning that those Member States started implementing Regulation (EU) No 379/2014 on 21 April 2017.
Operators/aircraft that fall under Regulation (EU) No 965/2012:
- Operators who have their principal place of business (for companies) or reside (for natural persons) in a EU MS regardless of the State of Registry of their aircraft; and
- Aircraft used in commercial SPO operations must have a C of A in accordance with Regulation (EU) No 748/2012, meaning the aircraft must be registered in an EU Member State. Alternatively, the aircraft may be under a wet lease-in or a dry lease-in agreement. In those cases, the aircraft may remain in a third country register. There are however certain conditions that have to be met before the operator may lease-in third country registered aircraft. There is no requirement for aircraft registration in non-commercial SPO operations.
Operators/operations/aircraft that do not fall under Regulation (EU) No 965/2012, but are regulated in accordance with Member States national legislation:
- Specialised commercial and non-commercial operations of aircraft falling under Annex I to Regulation (EU) 2018/1139 (the Basic Regulation);
- Military, customs, police, search and rescue, firefighting, coastguard or similar activities or services
- Third-country operators of SPO commercial and non-commercial
Operations that fall under Part-SPO
- SPO non-commercial using complex aeroplanes and helicopters;
- All commercial SPO with aeroplanes and helicopters.
Operations and aircraft that do not fall under Part-SPO, but fall under Part-NCO
- Non-commercial SPO of non-complex aeroplanes and helicopters;
- Certain commercial SPO of non-complex aeroplanes and helicopters in accordance with SPO.GEN.005(c) such as:
1) competition flights or flying displays, on the condition that the remuneration or any valuable consideration given for such flights is limited to recovery of direct costs and a proportionate contribution to annual costs, as well as prizes of no more than a value specified by the competent authority;
- (see Reg. (EU) No 965/2012, Article 2 ‘Definitions’ for the definitions of ‘competition flights’ and ‘flying displays’);
- (see GM2 Art. 6.4a(a)(b) ‘Derogations’, EASA Decision 2014/019/R for the explanation of ‘direct cost’);
- (see GM3 Art. 6.4a(a)(b) ‘Derogations’, EASA Decision 2014/019/R for the explanation of ‘annual cost’);
and
2 ) parachute dropping, sailplane towing or aerobatic flights performed either by a training organisation having its principal place of business in a Member State and approved in accordance with Regulation (EU) No 1178/2011, or by an organisation created with the aim of promoting aerial sport or leisure aviation, on the condition that the aircraft is operated by the organisation on the basis of ownership or dry lease, that the flight does not generate profits distributed outside of the organisation, and that whenever non-members of the organisation are involved, such flights represent only a marginal activity of the organisation.
- (see GM2 Art. 6.4a(c) ‘Derogations’, EASA Decision 2014/019/R for the explanation of the term ‘marginal activity’).
Part-SPO includes the implementing rules (IRs) for commercial specialised air operations with complex and non-complex aeroplanes and helicopters and for non-commercial specialised air operations with complex aeroplanes and helicopters.
The associated Decisions containing the Acceptable Means of Compliance (AMC) and Guidance Material (GM) are published on the EASA website.
Diagrams illustrating the rule structure are available here.
Specialised operations with balloons – both commercial and non-commercial – are governed by Reg. (EU) 2018/395 laying down detailed rules for the operation of balloons.
Specialised operations with sailplanes – both commercial and non-commercial – are governed by Reg. (EU) 2018/1976 laying down detailed rules for the operation of sailplanes.
More details on the regulations page, including links to the EASA AMC and GM.
Commercial and non-commercial SPO with complex aeroplanes and helicopters may be conducted as soon as the SPO operator submits a declaration to its competent authority. None of those operations is subject to an Air Operator Certificate.
Some commercial SPO of high risk, especially for third parties on the ground, would need to be authorised by the competent authority. An operator who engages in such ‘high risk commercial SPO must therefore apply for an authorisation, in addition to the declaration it has submitted.
"High risk commercial specialised operation” means:
- any commercial specialised aircraft operation carried out over an area where the safety of third parties on the ground is likely to be endangered in the event of an emergency, or
- as determined by the competent authority of the place where the operation is conducted, any commercial specialised aircraft operation that, due to its specific nature and the local environment in which it is conducted, poses a high risk, in particular to third parties on the ground.
A list of ‘high-risk commercial specialised operations’ of Member States is available below in ‘Related Content’.
Non-commercial specialised operations with other than complex motor-powered aircraft do not submit declarations.
Rule applicability for SPO:
| SPO | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Rule applicability |
COM |
NCC |
NCO |
| Cover Regulation |
|
|
|
| Definitions | |||
| Part-ARO | - | - | - |
| Part-ORO | - | ||
| Part-CAT | - | - | - |
| Part-SPA | |||
| Part-NCC | - | - | - |
| Part-NCO | - | - | |
| Part-SPO | |||
- SPO (COM)
- Commercial specialised operations with complex and non-complex aircraft
- SPO (NCC)
- Non-commercial specialised operations with complex aircraft
- SPO (NCO)
- Non-commercial specialised operations with non-complex aircraft
Part-SPO: structure
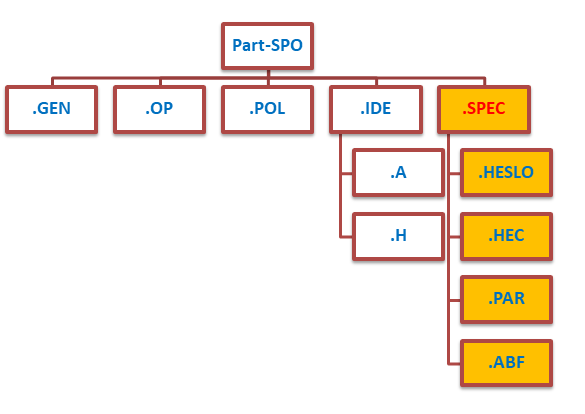
- .GEN – general requirements
- .OP – operational procedures
- .POL – performance and operating limitations
- .IDE – instruments, data, equipment
- .A, .H, - aeroplanes, helicopters
- .SPEC – specific requirements
- .HESLO – helicopter external sling load operations
- .HEC – human external cargo operations
- .PAR – parachute operations
- .ABF – aerobatic flights
Part-ORO: applicability of subparts to SPO operators
| Part-ORO |
Operator |
|
|---|---|---|
|
SPO (COM) |
SPO (NCC) |
|
|
.GEN |
||
|
.AOC |
- | - |
|
.DEC |
||
|
.SPO |
- | |
|
.MLR |
- | |
|
.SEC |
||
|
.FC |
|
|
|
.CC |
- | - |
|
.TC |
- | |
|
.FTL |
- | - |
| Applicable | |
| Partly applicable |
Part-SPA: applicability of subparts to SPO operators
| Part-SPA | SPO Operator |
|---|---|
|
.GEN |
|
|
.PBN |
|
|
.MNPS |
|
|
.RVSM |
|
|
.LVO |
|
|
.ETOPS |
- |
|
.DG |
|
|
.NVIS |
- |
|
.HHO |
- |
|
.HEMS |
- |
| Applicable |