CS ACNS.A.GEN.001 Applicability
ED Decision 2022/008/R/R
These certification specifications provide standards for the certification and approval of designs, or changes to designs of aircraft, allowing aircraft operators to comply with the applicable airspace requirements or mandatory equipage requirements in the areas of:
— — Communication, Navigation and Surveillance (CNS);
— — Terrain Awareness and Warning Systems (TAWS);
— — Reduced Vertical Separation Minima (RVSM); and
— — Location of an Aircraft in Distress (LAD / GADSS).
[Issue: CS-ACNS/2]
[Issue: CS-ACNS/4]
GM1 ACNS.A.GEN.001 Applicability
ED Decision 2022/008/R
A reference to compliance with the relevant section(s) of CS-ACNS in the aircraft flight manual (AFM) or other approved document may be used by operators to demonstrate compliance with the applicable airspace rules.
[Issue: CS-ACNS/4]
ED Decision 2022/008/R
This point contains the definitions of terms used in CS-ACNS:
Accuracy is, in the context of PBN operations, the degree of conformance between the estimated, measured or desired position and/or the velocity of a platform at a given time, and its true position or velocity.
ADS-B refers to automatic dependent surveillance - broadcast, a surveillance technique in which aircraft automatically provide, via a data link, data derived from on-board navigation and position-fixing systems. It refers to a surveillance technology where ADS-B Out equipped aircraft broadcast position, altitude, velocity, and other information in support of both air-to-ground and air-to-air surveillance applications.
ADS-B device failure refers to a condition announced to the flight crew whereby the ADS-B transmit unit is unable to transmit ADS-B messages.
ADS-B function failure refers to a condition announced to the flight crew whereby the position source(s) or interconnecting avionics fail to provide horizontal position data to the ADS-B transmit unit.
ADS-B Out system refers to the overall set of avionics that generate, transport, process, and transmit ADS-B data.
ADS-B transmit unit refers to that part of the ADS-B Out system that resides within the transponder and transmits 1090 MHz ES ADS-B data, including the data processing within that system.
Advisory alerts refers to the level or category of alert for conditions that require flight crew awareness and may require subsequent flight crew response.
Advisory vertical navigation (‘Advisory VNAV’) is an area navigation system function guiding the aircraft on a vertical path calculated by the area navigation system on an approach procedure that has been designed as a 2D procedure.
Aircraft Identification is an alphanumeric chain that contains information allowing operational identification of individual flights. It contains either the Aircraft Identification as registered in item 7 of the flight plan or the aircraft registration if no flight plan has been filed.
Airship is a power-driven lighter-than-air aircraft.
Alert is a generic term used to describe a flight deck indication meant to attract the attention of and identify to the flight crew a non-normal operational or aeroplane system condition. Alerts are classified at levels or categories corresponding to Warning, Caution, and Advisory. Alert indications also include non-normal range markings (for example, exceedances on instruments and gauges).
Altimetry system error (ASE) refers to the difference between the altitude indicated by the altimeter display, assuming a correct altimeter barometric setting, and the pressure altitude corresponding to the undisturbed ambient pressure.
Area navigation (RNAV) is a method of navigation which permits aircraft operation on any desired flight path within the coverage of ground or space-based navigation aids or within the limits of the capability of self-contained aids, or a combination of these.
Aircraft-based augmentation system (ABAS) is an augmentation system that augments and/or integrates the information obtained from the GNSS core constellation elements with other information available on board the aircraft.
ATN B1 refers to Aeronautical Telecommunication Network Build 1.
ATS communications management service (ACM) is a service that provides automated assistance to flight crews and air traffic controllers for conducting the transfer of ATC communications (voice and data).
ATS clearance and information service (ACL) is a service that provides flight crews and controllers with the ability to conduct operational exchanges.
ATS microphone check service (AMC) is a service that provides air traffic controllers with the capability to send an instruction to one or several data link equipped aircraft, at the same time, in order to instruct flight crew(s) to verify that his/their voice communication equipment is not blocking a given voice channel.
Aural alert is a discrete sound, tone, or verbal statement used to annunciate a condition, situation, or event.
Automatic altitude control system is any system that is designed to automatically control the aircraft to a referenced pressure altitude.
Barometric altitude rate refers to the rate of climb estimated by using the difference of pressure.
Barometric pressure setting is the barometric pressure setting used by the pilot when flying the aircraft.
Comm-B refers to a 112-bit Mode S reply containing a 56-bit MB message field containing the extracted transponder register.
Caution refers to the level or category of alert for conditions that require immediate flight crew awareness and a less urgent subsequent flight crew response than a warning alert.
Continuity of function refers, in the context of PBN operations, to the capability of the system to perform its intended function without unscheduled interruptions.
Continuity (system continuity) is the probability that a system will perform its required function without unscheduled interruption, assuming that the system is available at the initiation of the intended operation.
Controlled flight into terrain (CFIT) is an accident or incident in which an aircraft, under the full control of the pilot, is flown into terrain, obstacles, or water.
CPDLC is the ICAO standardised procedure for Controller-Pilot Data Link Communications. CPDLC takes the form of an application, present on both aircraft and ground-based ATC centres that provides support for the Data Link Communications Initiation Capability (DLIC), ATS communications management service (ACM), ATS Clearance and Information service (ACL) and ATS microphone check service (AMC).
Data link is a communication technology where ‘Data Link’ equipped aircraft communicate with ‘Data Link’ capable ground units to exchange digital information (bi-directional exchange).
Data link communications initiation capability (DLIC) is a service that enables the exchange of the necessary information for the establishment of data link communications between the ground and aircraft data link systems.
Data quality indicator refers to integrity and/or accuracy quality metrics that are associated with some of the ADS-B Out surveillance data, in particular with the horizontal position.
Defined path is the output of the path definition function of the RNP System.
Desired path is the path that the flight crew and air traffic control can expect the aircraft to fly, given a particular route leg or transition.
Distance-measuring equipment (DME) refers to a ground–airborne positioning system based on interrogations from an airborne interrogator and replies from a ground-based transponder, that allows the aircraft to measure its slant range from the position of the ground-based DME transponder.
Downlink is a transfer of information, generated by an aircraft (not necessarily airborne) and sent to the ground for further processing by an ATC Centre.
Emergency indicators refers to specific Mode A Code values: 7500 unlawful interference, 7600 radio failure, 7700 general emergency.
Failure condition terms are defined in AMC 25.1309, FAA AC 23.1309-1( ), AC 27-1B or AC 29-2C.
FANS 1/A refers to Future Air Navigation System 1 or Future Air Navigation System A.
False alert is an incorrect or spurious alert caused by a failure of the alerting system including the sensor.
Field of view refers to either the optimum or maximum vertical and horizontal visual fields from the design eye reference point that can be accommodated with eye rotation only, as described in the figure below.
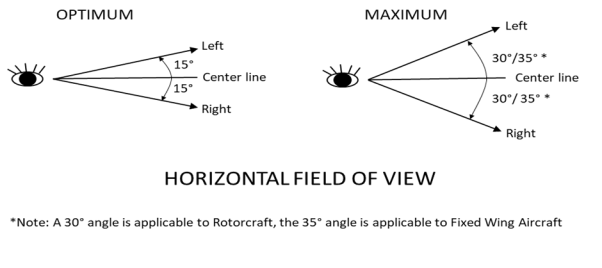
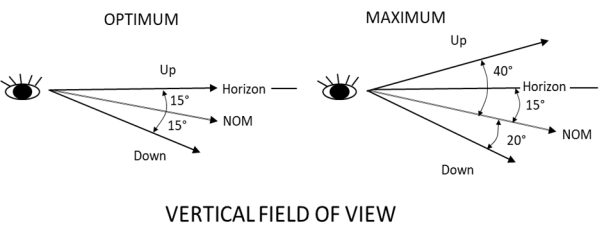
Figure 1 – Optimum and maximum fields of view
Note: This CS defines the optimum and maximum fields of view. As the Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) defines primary and secondary fields of view in its Advisory Circular (AC) 29-2C, ‘optimum’ should be read as primary and ‘maximum’ as secondary fields of view.
Flight plan is, in the context of PBN operations, a set of route segments and flight procedures defined and activated by the flight crew in the required navigation performance (RNP) system, relative to an intended flight or a portion of a flight of an aircraft.
FMS selected altitude refers to the level altitude used by the FMS to manage the vertical profile of the aircraft.
Forward looking terrain avoidance (FLTA) looks ahead of the aeroplane along and below the aeroplane’s lateral and vertical flight path and provides suitable alerts if a potential CFIT exists.
Global navigation satellite system (GNSS) refers to a worldwide position and time determination system that includes one or more satellite constellations, aircraft receivers and system integrity monitoring.
Ground Comm-B refers to a protocol which allows the interrogator to extract Comm‑B replies containing data from a defined source.
Ground speed is the speed of an aircraft relative to the surface, or relative to a horizontal plane at present position.
Group aircraft is a group of aircraft with similar altitude keeping equipment configurations and performance characteristics that are combined together for the purposes of statistical generic performance evaluation. Typically group aircraft refers to aircraft constructed to the same Type Certificate, Service Bulletin or Supplementary Type Certificate.
Hazard refers to a state or set of conditions that together with other conditions in the environment can lead to an accident.
Holding is a predetermined manoeuvre which keeps an aircraft within a specified airspace.
Horizontal velocity refers to the ground speed vector information.
ICAO 24-bit aircraft address is a technical address used by Mode S protocols to identify the transponder on the 1030/1090 MHz RF network. Each aircraft uses a unique 24-bit aircraft address allocated by their state of registry. This address may also be used by other types of avionics equipment for other purpose.
Inertial navigation system/inertial reference unit (INS/IRU) is an aircraft position sensor relying on accelerometers and gyroscopes to estimate position, direction and velocity.
Inertial vertical velocity is the rate of climb measure along the axis estimated using different sources including inertial reference.
Instrument landing system (ILS) is a system using ground-based transmitters and airborne receivers to provide lateral (‘localiser’) and vertical (’glide slope’) guidance to the runway.
Integrity (system integrity) is measured as the probability per operating hour of an undetected failure of a functional element that results in corrupted (erroneous) data, or a failure in the processing as specified, leading to the (partial) loss of otherwise available data.
Lateral navigation (LNAV) refers to area navigation in the horizontal plane.
Magnetic Heading is the angle between the aircraft centreline and magnetic North (angle between the direction to which the aircraft nose is pointing and the magnetic North).
MCP/FCU Selected Altitude is the level selected by the flight crew on the MCP or FCU of the aircraft. This altitude constitutes the level-off target input to the auto-pilot.
Mean sea level (MSL) is a reference for measuring and specifying altitudes in aeronautical information.
Mode S elementary surveillance refers to the use of Mode S surveillance data to downlink aircraft information from airborne installations.
Mode S enhanced surveillance refers to the use of other airborne information in addition to data used for Elementary Surveillance.
Navigation aid refers to a space- or ground-based facility that transmits signals that the aircraft’s navigation system may use to determine its position or its bearing.
Navigation functionality is the detailed capability of the navigation system required to meet the needs of the proposed operations in the airspace.
Navigation specification is a set of aircraft and aircrew requirements needed to support performance-based navigation operations within a defined airspace.
Non-group aircraft refers to an aircraft that is not a group aircraft but which is submitted for airworthiness approval on the characteristics of the unique airframe
Nuisance alert is an alert generated by a system that is functioning as designed but which is inappropriate or unnecessary for the particular condition.
Performance-based navigation (PBN) is area navigation based on performance requirements for aircraft operating along an ATS route, on an instrument approach procedure or in designated airspace.
Qualitative probability terms are defined in AMC 25.1309, FAA AC 23.1309-1( ), AC 27-1B or AC 29-2C.
Required obstacle clearance (ROC) refers to the required vertical clearance expressed in ft between an aircraft and an obstruction.
Required Terrain Clearance (RTC) is a terrain awareness and warning system (TAWS) FLTA mode that alerts when the aeroplane is above the terrain in the aeroplane’s projected flight path, but the projected amount of terrain clearance is considered unsafe for the particular phase of flight.
RNAV (X) specification refers to a navigation specification based on area navigation that does not include the requirement for on-board performance monitoring and alerting, designated by the prefix RNAV, where ‘X’ refers to the lateral navigation accuracy in nautical miles.
RNP (X) specification refers to a navigation specification based on area navigation that includes the requirement for on-board performance monitoring and alerting, designated by the prefix RNP, where ‘X’ refers to the lateral navigation accuracy in nautical miles or the operation type.
RNP system is a system that supports area navigation operations by integrating information from one or more positioning sensors and providing flight crew with the means to define a desired flight path.
Roll angle is the angle of wings compared to horizon representing the angle of rotation around the roll axis going along the centreline of the aircraft.
RVSM flight envelope may be considered to be in two parts; the basic RVSM flight envelope and the full RVSM flight envelope. The basic envelope includes those ranges of Mach numbers and gross weights at which the aircraft can most frequently be expected to operate at RVSM levels (i.e. FL 290 to FL 410 (or maximum attainable altitude)). The full envelope refers to the entire range of Mach numbers, gross weights and altitude values that the aircraft can be operated in RVSM airspace.
RVSM operational flight envelope is the Mach number, W/, and altitude ranges over which an aircraft can be operated in cruising flight within the RVSM airspace.
Satellite-based augmentation system (SBAS) is a wide coverage augmentation system which monitors the GNSS core constellation(s) and provides the user with augmentation information through a satellite-based transmitter.
Search volume is a volume of airspace around the aeroplane’s current and projected path that is used to define a TAWS alert condition.
Static source error (SSE) is the difference between the pressure sensed by the static system at the static port and the undisturbed ambient pressure.
Static source error correction (SSEC) is the correction for the residual static error to ensure compliance with performance requirements.
Terrain cell is a grid of terrain provided by the TAWS database which identifies the highest terrain elevation within a defined geographical area. Terrain cell dimensions and resolution can vary depending on the needs of the TAWS system and availability of data. If a supplier desires, obstacle height can be included in the terrain elevation.
Track is the projection on the earth’s surface of the path of an aircraft, the direction of which is usually expressed in degrees from north (true, magnetic or grid).
Track angle rate is the rate of change of the track angle.
Transmit refers to the provision of surveillance data by the transponder.
Transponder is a device that transmits airborne surveillance data spontaneously or when requested. The transmissions are performed on 1090 MHz RF band and the interrogations are received on 1030 MHz RF band using SSR/Mode S protocols. It is also named Secondary Surveillance Radar transponder.
Transponder level is an indication of which Mode S data-link protocols are supported by a transponder. There are 5 transponder levels defined by ICAO.
Transponder register is a transponder data buffer containing different pieces of information. It has 56 bits which are split in different fields. The definition of the transponder registers can be found in ICAO Doc 9871 edition 2 and in transponder MOPS ED-73E with the ICAO document being the reference document in case of conflict. Transponder registers are numbered in hexadecimal (00hex to FFhex). The register number is also known as the BDS code (Comm-B data selector). In this documentation a register is named: register XY16 or register addressed by BDS code X,Y. Outside this document, it is also often referenced as just BDS X,Y.
True track angle is the angle between the track (course over ground or path) of the aircraft and true north.
Uplink is a transfer of information, issued from any ground-based entity (typically: the ATC Centre under which the aircraft is under responsibility) to an aircraft (not necessarily airborne).
Vertical navigation (VNAV) refers to a method of navigation based on a computed vertical path.
VHF omnidirectional range (VOR) is a ground–airborne positioning system based on signals in space transmitted by the VOR ground station to the aircraft VOR receiver to measure its angular position from the ground station.
Warning refers to the level or category of alert for conditions that require immediate flight crew awareness and immediate flight crew response.
Worst case avionics is a combination of tolerance values, specified by the aircraft constructor for the altimetry fit into the aircraft, which gives the largest combined absolute value for residual SSE plus avionics errors.
[Issue: CS-ACNS/2]
[Issue: CS-ACNS/4]
CS ACNS.A.GEN.010 Instructions for continued airworthiness
ED Decision 2013/031/R
(See AMC1 ACNS.A.GEN.010)
Instructions for continued airworthiness for each system, part or appliance as specified in this CS ACNS and any information related to the interface of those systems, parts or appliances with the aircraft are to be provided
AMC1 ACNS.A.GEN.010 Instructions for Continued Airworthiness
ED Decision 2013/031/R
(a) Transponder testing
The Instructions for Continued Airworthiness should include the following measures and precautions in order to minimise the possibility of causing nuisance warnings to ACAS equipped aircraft.
(1) When not required, ensure all transponders are selected to ‘OFF‘ or ‘Standby‘.
(2) Before starting any test, contact the local Air Traffic Control Unit and advise them of your intention to conduct transponder testing. Advise the Air Traffic Unit of your start time and test duration. Also inform them of the altitude(s) at which you will be testing, your intended Aircraft Identification (Flight Id) and your intended Mode A code.
Note: Certain altitudes may not be possible due to over flying aircraft.
(3) Set the Mode A code to 7776 (or other Mode A code agreed with Air Traffic Control Unit).
Note: The Mode A code 7776 is reserved for SSR ground transponder monitoring. This code may be used for transponder testing after having received agreement from the Air Traffic Control Unit.
(4) Set the Aircraft Identification (Flight Id) with the first 8 characters of the company name. This is the name of the company conducting the tests.
(5) Set the on-the-ground status for all Mode S replies, except when an airborne reply is required (e.g. for altitude testing).
(6) Where possible, perform the testing inside a hangar to take advantage of any shielding properties it may provide.
(7) As a precaution, use antenna transmission covers whether or not testing is performed inside or outside.
(8) When testing the altitude (Mode C or S) parameter, radiate directly into the ramp test set via the prescribed attenuator.
(9) In between testing, i.e., to transition from one altitude to another, select the transponder to ‘standby’ mode.
(10) If testing transponder parameters other than ‘altitude‘, set altitude to minus 300 m (minus 1 000 feet) or over 18 250 m (60 000 feet). This will minimise the possibility of ACAS warning to airfield and overflying aircraft.
(11) When testing is complete, select the transponder(s) to ‘OFF‘ or ‘Standby’.
(b) Reduced Vertical Separation Minima
When developing the instructions for continued airworthiness, attention should be given to the following items:
(1) All RVSM equipment should be maintained in accordance with the component manufacturers' maintenance instructions and the performance criteria of the RVSM approval data package.
(2) Any repairs, not covered by approved maintenance documents, that may affect the integrity and accuracy of the altimeter system , e.g. those affecting the alignment of pitot/static probes, repairs to dents or deformation around static plates should be subject to a design review which is acceptable to the competent authority.
(3) Airframe geometry or skin waviness checks should be performed following repairs or alterations which have an effect on airframe surface and airflow.
(4) The maintenance and inspection programme for the autopilot should ensure continued accuracy and integrity of the automatic altitude control system.
CS ACNS.A.GEN.015 Aircraft documentation
ED Decision 2019/011/R
(a) The aircraft flight manual (AFM), or similar documentation approved by EASA, provides the list of aircraft capabilities for which the aircraft is certified in accordance with this CS.
(b) If there are deviations from this CS which result in limitation(s), they are to be clearly stated in the AFM or similar documentation approved by EASA.
[Issue: CS-ACNS/2]
AMC1 ACNS.A.GEN.015(a) Aircraft documentation
ED Decision 2019/011/R
An acceptable means of compliance in the case of aircraft PBN capabilities is to specify in the documentation which of the following navigation specifications and functionalities the aircraft is certified for:
(a) RNAV 10,
(b) RNAV 5,
(c) RNAV 2,
(d) RNAV 1,
(e) RNP 4,
(f) RNP 2,
(g) RNP 1,
(h) RNP 0.3,
(i) A-RNP,
(j) RNP APCH,
(k) RNP AR (for approach and/or departures),
(l) RF (specify the associated navigation specifications),
(m) FRT,
(n) parallel offset.
[Issue: CS-ACNS/2]
CS ACNS.A.GEN.020 Deviation from equipment standards
ED Decision 2019/011/R
Any deviations from the ETSO referenced in this CS and associated AMC are to be evaluated to ensure compliance with the CS requirements.
[Issue: CS-ACNS/2]
